multiplication : c <- beta c + alpha A b More...
Public Member Functions | |
| subroutine | susmm (order, transA, nrhs, alpha, A, b, ldb, c, ldc, istat) |
Multiply by a dense matrix (aka multi-vector). Either of 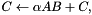 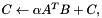 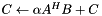 , depending on the value of , depending on the value of transA. More... | |
| subroutine | dusmm (order, transA, nrhs, alpha, A, b, ldb, c, ldc, istat) |
Multiply by a dense matrix (aka multi-vector). Either of 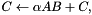 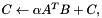 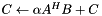 , depending on the value of , depending on the value of transA. More... | |
| subroutine | cusmm (order, transA, nrhs, alpha, A, b, ldb, c, ldc, istat) |
Multiply by a dense matrix (aka multi-vector). Either of 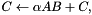 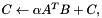 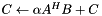 , depending on the value of , depending on the value of transA. More... | |
| subroutine | zusmm (order, transA, nrhs, alpha, A, b, ldb, c, ldc, istat) |
Multiply by a dense matrix (aka multi-vector). Either of 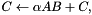 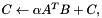 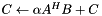 , depending on the value of , depending on the value of transA. More... | |
Detailed Description
multiplication : c <- beta c + alpha A b
- Parameters
-
istat The return code will be written to istat(this is a Fortran routine): either 0 (success) or -1 (failure).
Member Function/Subroutine Documentation
◆ cusmm()
| subroutine blas_sparse::usmm::cusmm | ( | integer | order, |
| integer | transA, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_idx_kind) | nrhs, | ||
| complex(kind(1.e0)) | alpha, | ||
| integer | A, | ||
| complex(kind(1.e0)), dimension (:,:) | b, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_idx_kind) | ldb, | ||
| complex(kind(1.e0)), dimension (:,:) | c, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_idx_kind) | ldc, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_ist_kind), intent(out) | istat | ||
| ) |
Multiply by a dense matrix (aka multi-vector). Either of 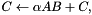
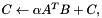
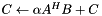 , depending on the value of
, depending on the value of transA.
- Parameters
-
order layour of the dense array. transA Transposition operator for matrix A. nrhs Number of right hand side columns. A A valid matrix handle. alpha Value for 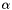 .
. b Dense vector b. ldb Leading dimension of b. c Dense vector c. ldc Leading dimension of c.
- Note
-
By setting the
blas_rsb_autotune_next_operationproperty via BLAS_ussp (at any time) the next multiplication routine call (either of BLAS_dusmv, BLAS_susmv, BLAS_zusmv, BLAS_cusmv, BLAS_dusmm, BLAS_susmm, BLAS_zusmm, BLAS_cusmm) will invoke autotuning before carrying out the effective operation. The tuning will take in account parameters like transposition, number of right hand sides, and scaling constants. By setting theblas_rsb_spmv_autotuning_onproperty via BLAS_ussp, the default number of executing threads for this matrix will be determined once, at matrix assembly time, and employed irrespective of the default threads count (different values for transposed and untransposed multiply). This can be overridden only by setting theRSB_NUM_THREADSenvironment variable.
- See also
- On the topic of autotuning, see also rsb_tune_spmm. If
–enable-rsb-num-threadshas been specified at configure time, theRSB_NUM_THREADSenvironment variable will override the number of executing threads specified byOMP_NUM_THREADS. (See also RSB_IO_WANT_EXECUTING_THREADS).
- Returns
- On success, 0 is returned; on error, -1.
- Parameters
-
istat The return code will be written to istat(this is a Fortran routine): either 0 (success) or -1 (failure).
◆ dusmm()
| subroutine blas_sparse::usmm::dusmm | ( | integer | order, |
| integer | transA, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_idx_kind) | nrhs, | ||
| real(kind(1.d0)) | alpha, | ||
| integer | A, | ||
| real(kind(1.d0)), dimension (:,:) | b, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_idx_kind) | ldb, | ||
| real(kind(1.d0)), dimension (:,:) | c, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_idx_kind) | ldc, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_ist_kind), intent(out) | istat | ||
| ) |
Multiply by a dense matrix (aka multi-vector). Either of 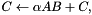
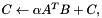
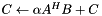 , depending on the value of
, depending on the value of transA.
- Parameters
-
order layour of the dense array. transA Transposition operator for matrix A. nrhs Number of right hand side columns. A A valid matrix handle. alpha Value for 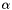 .
. b Dense vector b. ldb Leading dimension of b. c Dense vector c. ldc Leading dimension of c.
- Note
-
By setting the
blas_rsb_autotune_next_operationproperty via BLAS_ussp (at any time) the next multiplication routine call (either of BLAS_dusmv, BLAS_susmv, BLAS_zusmv, BLAS_cusmv, BLAS_dusmm, BLAS_susmm, BLAS_zusmm, BLAS_cusmm) will invoke autotuning before carrying out the effective operation. The tuning will take in account parameters like transposition, number of right hand sides, and scaling constants. By setting theblas_rsb_spmv_autotuning_onproperty via BLAS_ussp, the default number of executing threads for this matrix will be determined once, at matrix assembly time, and employed irrespective of the default threads count (different values for transposed and untransposed multiply). This can be overridden only by setting theRSB_NUM_THREADSenvironment variable.
- See also
- On the topic of autotuning, see also rsb_tune_spmm. If
–enable-rsb-num-threadshas been specified at configure time, theRSB_NUM_THREADSenvironment variable will override the number of executing threads specified byOMP_NUM_THREADS. (See also RSB_IO_WANT_EXECUTING_THREADS).
- Returns
- On success, 0 is returned; on error, -1.
- Parameters
-
istat The return code will be written to istat(this is a Fortran routine): either 0 (success) or -1 (failure).
◆ susmm()
| subroutine blas_sparse::usmm::susmm | ( | integer | order, |
| integer | transA, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_idx_kind) | nrhs, | ||
| real(kind(1.e0)) | alpha, | ||
| integer | A, | ||
| real(kind(1.e0)), dimension (:,:) | b, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_idx_kind) | ldb, | ||
| real(kind(1.e0)), dimension (:,:) | c, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_idx_kind) | ldc, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_ist_kind), intent(out) | istat | ||
| ) |
Multiply by a dense matrix (aka multi-vector). Either of 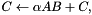
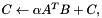
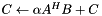 , depending on the value of
, depending on the value of transA.
- Parameters
-
order layour of the dense array. transA Transposition operator for matrix A. nrhs Number of right hand side columns. A A valid matrix handle. alpha Value for 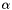 .
. b Dense vector b. ldb Leading dimension of b. c Dense vector c. ldc Leading dimension of c.
- Note
-
By setting the
blas_rsb_autotune_next_operationproperty via BLAS_ussp (at any time) the next multiplication routine call (either of BLAS_dusmv, BLAS_susmv, BLAS_zusmv, BLAS_cusmv, BLAS_dusmm, BLAS_susmm, BLAS_zusmm, BLAS_cusmm) will invoke autotuning before carrying out the effective operation. The tuning will take in account parameters like transposition, number of right hand sides, and scaling constants. By setting theblas_rsb_spmv_autotuning_onproperty via BLAS_ussp, the default number of executing threads for this matrix will be determined once, at matrix assembly time, and employed irrespective of the default threads count (different values for transposed and untransposed multiply). This can be overridden only by setting theRSB_NUM_THREADSenvironment variable.
- See also
- On the topic of autotuning, see also rsb_tune_spmm. If
–enable-rsb-num-threadshas been specified at configure time, theRSB_NUM_THREADSenvironment variable will override the number of executing threads specified byOMP_NUM_THREADS. (See also RSB_IO_WANT_EXECUTING_THREADS).
- Returns
- On success, 0 is returned; on error, -1.
- Parameters
-
istat The return code will be written to istat(this is a Fortran routine): either 0 (success) or -1 (failure).
◆ zusmm()
| subroutine blas_sparse::usmm::zusmm | ( | integer | order, |
| integer | transA, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_idx_kind) | nrhs, | ||
| complex(kind(1.d0)) | alpha, | ||
| integer | A, | ||
| complex(kind(1.d0)), dimension (:,:) | b, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_idx_kind) | ldb, | ||
| complex(kind(1.d0)), dimension (:,:) | c, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_idx_kind) | ldc, | ||
| integer(kind=rsb_blas_ist_kind), intent(out) | istat | ||
| ) |
Multiply by a dense matrix (aka multi-vector). Either of 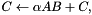
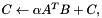
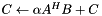 , depending on the value of
, depending on the value of transA.
- Parameters
-
order layour of the dense array. transA Transposition operator for matrix A. nrhs Number of right hand side columns. A A valid matrix handle. alpha Value for 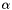 .
. b Dense vector b. ldb Leading dimension of b. c Dense vector c. ldc Leading dimension of c.
- Note
-
By setting the
blas_rsb_autotune_next_operationproperty via BLAS_ussp (at any time) the next multiplication routine call (either of BLAS_dusmv, BLAS_susmv, BLAS_zusmv, BLAS_cusmv, BLAS_dusmm, BLAS_susmm, BLAS_zusmm, BLAS_cusmm) will invoke autotuning before carrying out the effective operation. The tuning will take in account parameters like transposition, number of right hand sides, and scaling constants. By setting theblas_rsb_spmv_autotuning_onproperty via BLAS_ussp, the default number of executing threads for this matrix will be determined once, at matrix assembly time, and employed irrespective of the default threads count (different values for transposed and untransposed multiply). This can be overridden only by setting theRSB_NUM_THREADSenvironment variable.
- See also
- On the topic of autotuning, see also rsb_tune_spmm. If
–enable-rsb-num-threadshas been specified at configure time, theRSB_NUM_THREADSenvironment variable will override the number of executing threads specified byOMP_NUM_THREADS. (See also RSB_IO_WANT_EXECUTING_THREADS).
- Returns
- On success, 0 is returned; on error, -1.
- Parameters
-
istat The return code will be written to istat(this is a Fortran routine): either 0 (success) or -1 (failure).
The documentation for this interface was generated from the following file:
 1.8.13
1.8.13