The reference documentation of the librsb library comes in both HTML and Unix man pages formats.
The following sections/man pages are available: The librsb library interface (rsb.h, optional ones rsb.hpp and rsb.F90) ; The Sparse BLAS interface to librsb (blas_sparse.h, rsb_blas_sparse.F90) ; Example programs and code.
More...
Macros | |
| #define | RSB_SIZEOF(TYPE) RSB_NUMERICAL_TYPE_SIZE(TYPE) |
Functions | |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_lib_init (struct rsb_initopts *iop) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_lib_set_opt (enum rsb_opt_t iof, const void *iop) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_lib_get_opt (enum rsb_opt_t iof, void *iop) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_lib_set_opt_str (const rsb_char_t *opnp, const rsb_char_t *opvp) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_lib_reinit (struct rsb_initopts *iop) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_lib_exit (struct rsb_initopts *iop) |
| struct rsb_mtx_t * | rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_const (const void *VA, const rsb_coo_idx_t *IA, const rsb_coo_idx_t *JA, rsb_nnz_idx_t nnzA, rsb_type_t typecode, rsb_coo_idx_t nrA, rsb_coo_idx_t ncA, rsb_blk_idx_t brA, rsb_blk_idx_t bcA, rsb_flags_t flagsA, rsb_err_t *errvalp) |
| struct rsb_mtx_t * | rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_inplace (void *VA, rsb_coo_idx_t *IA, rsb_coo_idx_t *JA, rsb_nnz_idx_t nnzA, rsb_type_t typecode, rsb_coo_idx_t nrA, rsb_coo_idx_t ncA, rsb_blk_idx_t brA, rsb_blk_idx_t bcA, rsb_flags_t flagsA, rsb_err_t *errvalp) |
| struct rsb_mtx_t * | rsb_mtx_free (struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_clone (struct rsb_mtx_t **mtxBpp, rsb_type_t typecode, rsb_trans_t transA, const void *alphap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, rsb_flags_t flags) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_spmv (rsb_trans_t transA, const void *alphap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, const void *Xp, rsb_coo_idx_t incX, const void *betap, void *Yp, rsb_coo_idx_t incY) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_spsv (rsb_trans_t transT, const void *alphap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxTp, const void *Xp, rsb_coo_idx_t incX, void *Yp, rsb_coo_idx_t incY) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_spsm (rsb_trans_t transT, const void *alphap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxTp, rsb_coo_idx_t nrhs, rsb_flags_t order, const void *betap, const void *Bp, rsb_nnz_idx_t ldB, void *Cp, rsb_nnz_idx_t ldC) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_coo_sort (void *VA, rsb_coo_idx_t *IA, rsb_coo_idx_t *JA, rsb_nnz_idx_t nnzA, rsb_coo_idx_t nrA, rsb_coo_idx_t ncA, rsb_type_t typecode, rsb_flags_t flagsA) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_coo_cleanup (rsb_coo_idx_t *nnzp, void *VA, rsb_coo_idx_t *IA, rsb_coo_idx_t *JA, rsb_nnz_idx_t nnzA, rsb_coo_idx_t nrA, rsb_coo_idx_t ncA, rsb_type_t typecode, rsb_flags_t flagsA) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_file_mtx_get_dims (const char *filename, rsb_coo_idx_t *nrp, rsb_coo_idx_t *ncp, rsb_coo_idx_t *nzp, rsb_flags_t *flagsp) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_perror (void *stream, rsb_err_t errval) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_strerror_r (rsb_err_t errval, rsb_char_t *buf, size_t buflen) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_upd_vals (struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, enum rsb_elopf_t elop_flags, const void *omegap) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_set_vals (struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, const void *VA, const rsb_coo_idx_t *IA, const rsb_coo_idx_t *JA, rsb_nnz_idx_t nnz, rsb_flags_t flags) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_get_vals (const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, void *VA, const rsb_coo_idx_t *IA, const rsb_coo_idx_t *JA, rsb_nnz_idx_t nnz, rsb_flags_t flags) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_file_mtx_save (const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, const rsb_char_t *filename) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_file_vec_save (const rsb_char_t *filename, rsb_type_t typecode, const void *Yp, rsb_coo_idx_t yvl) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_file_vec_load (const rsb_char_t *filename, rsb_type_t typecode, void *Yp, rsb_coo_idx_t *yvlp) |
| struct rsb_mtx_t * | rsb_file_mtx_load (const rsb_char_t *filename, rsb_flags_t flagsA, rsb_type_t typecode, rsb_err_t *errvalp) |
| struct rsb_mtx_t * | rsb_sppsp (rsb_type_t typecode, rsb_trans_t transA, const void *alphap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, rsb_trans_t transB, const void *betap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxBp, rsb_err_t *errvalp) |
| struct rsb_mtx_t * | rsb_spmsp (rsb_type_t typecode, rsb_trans_t transA, const void *alphap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, rsb_trans_t transB, const void *betap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxBp, rsb_err_t *errvalp) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_add_to_dense (const void *alphap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, rsb_nnz_idx_t ldB, rsb_nnz_idx_t nrB, rsb_nnz_idx_t ncB, rsb_bool_t rowmajorB, void *Bp) |
| rsb_trans_t | rsb_psblas_trans_to_rsb_trans (const char psbtrans) |
| struct rsb_mtx_t * | rsb_mtx_alloc_from_csr_const (const void *VA, const rsb_coo_idx_t *RP, const rsb_coo_idx_t *JA, rsb_nnz_idx_t nnzA, rsb_type_t typecode, rsb_coo_idx_t nrA, rsb_coo_idx_t ncA, rsb_blk_idx_t brA, rsb_blk_idx_t bcA, rsb_flags_t flagsA, rsb_err_t *errvalp) |
| struct rsb_mtx_t * | rsb_mtx_alloc_from_csc_const (const void *VA, const rsb_coo_idx_t *IA, const rsb_coo_idx_t *CP, rsb_nnz_idx_t nnzA, rsb_type_t typecode, rsb_coo_idx_t nrA, rsb_coo_idx_t ncA, rsb_blk_idx_t brA, rsb_blk_idx_t bcA, rsb_flags_t flagsA, rsb_err_t *errvalp) |
| struct rsb_mtx_t * | rsb_mtx_alloc_from_csr_inplace (void *VA, rsb_nnz_idx_t *RP, rsb_coo_idx_t *JA, rsb_nnz_idx_t nnzA, rsb_type_t typecode, rsb_coo_idx_t nrA, rsb_coo_idx_t ncA, rsb_blk_idx_t brA, rsb_blk_idx_t bcA, rsb_flags_t flagsA, rsb_err_t *errvalp) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_switch_to_csr (struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, void **VAp, rsb_coo_idx_t **IAp, rsb_coo_idx_t **JAp, rsb_flags_t flags) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_get_coo (const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, void *VA, rsb_coo_idx_t *IA, rsb_coo_idx_t *JA, rsb_flags_t flags) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_get_csr (rsb_type_t typecode, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, void *VA, rsb_nnz_idx_t *RP, rsb_coo_idx_t *JA, rsb_flags_t flags) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_get_rows_sparse (rsb_trans_t transA, const void *alphap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, void *VA, rsb_coo_idx_t *IA, rsb_coo_idx_t *JA, rsb_coo_idx_t frA, rsb_coo_idx_t lrA, rsb_nnz_idx_t *rnzp, rsb_flags_t flags) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_get_coo_block (const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, void *VA, rsb_coo_idx_t *IA, rsb_coo_idx_t *JA, rsb_coo_idx_t frA, rsb_coo_idx_t lrA, rsb_coo_idx_t fcA, rsb_coo_idx_t lcA, const rsb_coo_idx_t *IREN, const rsb_coo_idx_t *JREN, rsb_nnz_idx_t *rnzp, rsb_flags_t flags) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_spmm (rsb_trans_t transA, const void *alphap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, rsb_coo_idx_t nrhs, rsb_flags_t order, const void *Bp, rsb_nnz_idx_t ldB, const void *betap, void *Cp, rsb_nnz_idx_t ldC) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_spmsp_to_dense (rsb_type_t typecode, rsb_trans_t transA, const void *alphap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, rsb_trans_t transB, const void *betap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxBp, rsb_nnz_idx_t ldC, rsb_nnz_idx_t nrC, rsb_nnz_idx_t ncC, rsb_bool_t rowmajorC, void *Cp) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_rndr (const char *filename, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, rsb_coo_idx_t pmWidth, rsb_coo_idx_t pmHeight, rsb_marf_t rflags) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_file_mtx_rndr (void *pmp, const char *filename, rsb_coo_idx_t pmlWidth, rsb_coo_idx_t pmWidth, rsb_coo_idx_t pmHeight, rsb_marf_t rflags) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_switch_to_coo (struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, void **VAp, rsb_coo_idx_t **IAp, rsb_coo_idx_t **JAp, rsb_flags_t flags) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_get_prec (void *opdp, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, rsb_precf_t prec_flags, const void *ipdp) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_get_info (const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, enum rsb_mif_t miflags, void *minfop) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_get_info_str (const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, const rsb_char_t *mis, void *minfop, size_t buflen) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_get_nrm (const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, void *Np, enum rsb_extff_t flags) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_get_vec (const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, void *Dp, enum rsb_extff_t flags) |
| rsb_time_t | rsb_time (void) |
| struct rsb_mtx_t * | rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_begin (rsb_nnz_idx_t nnzA, rsb_type_t typecode, rsb_coo_idx_t nrA, rsb_coo_idx_t ncA, rsb_flags_t flagsA, rsb_err_t *errvalp) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_end (struct rsb_mtx_t **mtxApp) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_tune_spmm (struct rsb_mtx_t **mtxOpp, rsb_real_t *sfp, rsb_int_t *tnp, rsb_int_t maxr, rsb_time_t maxt, rsb_trans_t transA, const void *alphap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, rsb_coo_idx_t nrhs, rsb_flags_t order, const void *Bp, rsb_nnz_idx_t ldB, const void *betap, void *Cp, rsb_nnz_idx_t ldC) |
| rsb_err_t | rsb_tune_spsm (struct rsb_mtx_t **mtxOpp, rsb_real_t *sfp, rsb_int_t *tnp, rsb_int_t maxr, rsb_time_t maxt, rsb_trans_t transA, const void *alphap, const struct rsb_mtx_t *mtxAp, rsb_coo_idx_t nrhs, rsb_flags_t order, const void *Bp, rsb_nnz_idx_t ldB, const void *betap, void *Cp, rsb_nnz_idx_t ldC) |
Detailed Description
The reference documentation of the librsb library comes in both HTML and Unix man pages formats.
The following sections/man pages are available: The librsb library interface (rsb.h, optional ones rsb.hpp and rsb.F90) ; The Sparse BLAS interface to librsb (blas_sparse.h, rsb_blas_sparse.F90) ; Example programs and code.
In general, users of this library are interested in high performance sparse matrix computations on cache based shared memory parallel computers.
For this, librsb offers a native C interface (here documented) and a Fortran one (in rsb.F90, equivalent to the C declaration headers from rsb.h), in addition to the Sparse BLAS one (both C and Fortran, documented).
Please refer to optional <rsb.hpp> for the C++ API.
Configuration, build, and installation instructions are contained in the README file distributed in the sources archive.
Typical C program structure
- initialize
librsbwith rsb_lib_init() - (in any order) allocate matrices (e.g.: with rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_inplace() or others); do any computation with them (e.g.: rsb_spmv(), rsb_spsv() ); converting matrices (e.g.: with rsb_mtx_switch_to_coo() ); freeing matrices (rsb_mtx_free() )
- finalize
librsbwith rsb_lib_exit()
Important usage notes
General C program structure Before calling any librsb function, a program is required to initialize librsb's internal status. This is done by calling rsb_lib_init() . Afterwards, any librsb function can be safely used. When librsb functions are not intended to be called anymore, a program may call rsb_lib_exit() to free any resource. Then, rsb_lib_init() should be called for further usage of librsb.
Manipulating matrices and vectors In order to use librsb, the user is not required to use explicitly any of librsb's data structures: their manipulation is to be performed by librsb functions. Therefore, knowledge of librsb's matrix type (rsb_mtx_t) is not necessary at all: this structure is intended to be used as an opaque container.
On the contrary, arrays for numerical vectors (or more generally, dense matrices) are expected to be managed by the user: librsb does not furnish any specific vector type. Computational functions treat dense vectors/matrices are simple arrays of a specified type; see the Example programs and code .
Computational functions This library can be configured at build time to support a custom subset of numerical types. To keep the programming interface compact, it has been decided to not replicate the computational functions to each numerical type. Instead, the type is expected to be specified by the user via a type flag. For instance, matrix assembly functions (e.g.: rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_const() ) accept a type information and keep it stored in the matrix structure. Therefore, computational functions (e.g.: rsb_spmv() ) can fetch this information from their rsb_mtx_t operand, and treat accordingly the other parameters (e.g.: alphap, Xp, ...). Mixed type operations are currently not supported.
Memory management
Matrix structures (rsb_mtx_t) allocated by librsb shall be freed only via rsb_mtx_free() .
Benchmarking
If you want to benchmark this library, there are different possibilities:
Tuning and Customization
There are different ./configure options you may look at for tuning or customizing the library.
Macro Definition Documentation
◆ RSB_SIZEOF
| #define RSB_SIZEOF | ( | TYPE | ) | RSB_NUMERICAL_TYPE_SIZE(TYPE) |
Use RSB_SIZEOF macro to get the size (in bytes) of a type supported by the library (e.g.: when allocating numerical vectors).
Enumeration Type Documentation
◆ rsb_elopf_t
| enum rsb_elopf_t |
Flags for specifying a particular elemental/row-wise operation with rsb_mtx_upd_vals().
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| RSB_ELOPF_MUL | Elemental multiplication of the matrix by a specified scalar (usable with rsb_mtx_upd_vals(), binary operation). |
| RSB_ELOPF_DIV | Elemental division by a specified scalar (usable with rsb_mtx_upd_vals(), binary operation). |
| RSB_ELOPF_POW | Elemental power to a specified scalar (usable with rsb_mtx_upd_vals(), binary operation). |
| RSB_ELOPF_NEG | Elemental negation (usable with rsb_mtx_upd_vals(), unary operation). |
| RSB_ELOPF_SCALE_ROWS | Row wise scaling by a specified scaling vector (usable with rsb_mtx_upd_vals(), binary operation). |
| RSB_ELOPF_SCALE_COLS | Column wise scaling by a specified scaling vector (usable with rsb_mtx_upd_vals(), binary operation). |
| RSB_ELOPF_SCALE_ROWS_REAL | Row wise scaling by a specified scaling vector. If matrix is of a complex type, the argument is expected to be of the corresponding real type (assumed that that type has been enabled). (usable with rsb_mtx_upd_vals(), binary operation). |
| RSB_ELOPF_SCALE_COLS_REAL | Column wise scaling by a specified scaling vector. If matrix is of a complex type, the argument is expected to be of the corresponding real type (assumed that that type has been enabled). (usable with rsb_mtx_upd_vals(), binary operation). |
◆ rsb_extff_t
| enum rsb_extff_t |
Extraction filter flags, to be used with rsb_mtx_get_nrm()/rsb_mtx_get_vec().
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| RSB_EXTF_NORM_ONE | rsb_mtx_get_nrm() flag value for computing the one-norm. |
| RSB_EXTF_NORM_TWO | rsb_mtx_get_nrm() flag value for computing the two-norm (Frobenius norm). |
| RSB_EXTF_NORM_INF | rsb_mtx_get_nrm() flag value for computing the infinity-norm. |
| RSB_EXTF_SUMS_ROW | rsb_mtx_get_vec() flag value for computing the sum along each row. |
| RSB_EXTF_SUMS_COL | rsb_mtx_get_vec() flag value for computing the sum along each column. |
| RSB_EXTF_ASUMS_ROW | rsb_mtx_get_vec() flag value for computing the absolute values sum, along each row. |
| RSB_EXTF_ASUMS_COL | rsb_mtx_get_vec() flag value for computing the absolute values sum, along each column. |
| RSB_EXTF_DIAG | rsb_mtx_get_vec() flag value for extracting the diagonal submatrix. |
◆ rsb_mif_t
| enum rsb_mif_t |
Flags for getting matrix information via rsb_mtx_get_info()/rsb_mtx_get_info_str().
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| RSB_MIF_INDEX_STORAGE_IN_BYTES__TO__SIZE_T | Index storage occupation, in bytes. (size_t) |
| RSB_MIF_INDEX_STORAGE_IN_BYTES_PER_NNZ__TO__RSB_REAL_T | Index storage occupation per nnz, in bytes. (rsb_real_t) |
| RSB_MIF_MATRIX_ROWS__TO__RSB_COO_INDEX_T | Rows count(rsb_coo_idx_t) |
| RSB_MIF_MATRIX_COLS__TO__RSB_COO_INDEX_T | Columns count (rsb_coo_idx_t) |
| RSB_MIF_MATRIX_NNZ__TO__RSB_NNZ_INDEX_T | Nonzeroes count (rsb_nnz_idx_t) |
| RSB_MIF_TOTAL_SIZE__TO__SIZE_T | Total size, in bytes (size_t) |
| RSB_MIF_MATRIX_FLAGS__TO__RSB_FLAGS_T | Matrix flags (rsb_flags_t) |
| RSB_MIF_MATRIX_TYPECODE__TO__RSB_TYPE_T | Matrix type code (rsb_type_t) |
| RSB_MIF_MATRIX_INFO__TO__CHAR_P | Matrix info string, only for rsb_mtx_get_info_str() (rsb_char_t*) |
| RSB_MIF_LEAVES_COUNT__TO__RSB_BLK_INDEX_T | Leaf submatrices count (rsb_blk_idx_t) |
◆ rsb_opt_t
| enum rsb_opt_t |
library option values for rsb_lib_init, rsb_lib_set_opt_str, rsb_lib_reinit, rsb_lib_exit, rsb_lib_get_opt, rsb_lib_set_opt, or (deprecated) macros RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_GET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_SET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_C_IOP..
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| RSB_IO_WANT_VERBOSE_INIT | RSB_IO_WANT_VERBOSE_INIT prompts for a verbose initialization of the library: messages will be written to the file descriptor ( |
| RSB_IO_WANT_VERBOSE_EXIT | RSB_IO_WANT_VERBOSE_EXIT prompts for a verbose finalization of the library: messages will be written to the file descriptor ( |
| RSB_IO_WANT_OUTPUT_STREAM | Specifies the default output stream. Output (debug info) info will be written to the file descriptor ( |
| RSB_IO_WANT_SORT_METHOD | Specifies the default sorting method. Specified as a pointed integer (rsb_int_t) number, in {[0],1}. (internal) |
| RSB_IO_WANT_CACHE_BLOCKING_METHOD | Specifies the default cache blocking method. Specified as a pointed integer (rsb_int_t) number, in {-1,[0],1}. (internal) |
| RSB_IO_WANT_SUBDIVISION_MULTIPLIER | Specifies a multiplier for finer (if >1.0) or coarser (if <1.0) subdivisions. Specified as a pointed (rsb_real_t) number, in {..,[1.0],..}. (internal) |
| RSB_IO_WANT_VERBOSE_ERRORS | Prompts for a verbose error reporting: messages will be written to the file descriptor ( |
| RSB_IO_WANT_BOUNDED_BOX_COMPUTATION | Prompts for bounded box computation, for a smoother submatrices locking; pointed rsb_int_t in {0,[1]}. (internal). |
| RSB_IO_WANT_EXECUTING_THREADS | Specifies the number of desired executing threads; pointed rsb_int_t in {[0],1,..}. |
| RSB_IO_WANT_EXTRA_VERBOSE_INTERFACE | Specifies the level of interface verbosity; if setting, pointed rsb_int_t values should be in {[0],1,..}. Support may be enabled or disabled at build time via the |
| RSB_IO_WANT_MEMORY_HIERARCHY_INFO_STRING | Specifies a custom memory hierarchy info string; pointed |
| RSB_IO_WANT_IS_INITIALIZED_MARKER | Used for getting whether the library has been initialized (RSB_BOOL_TRUE) or not (RSB_BOOL_FALSE) ; pointed |
| RSB_IO_WANT_MEM_ALLOC_CNT | Used for getting the count of memory allocations performed by librsb employing librsb's memory allocation wrapper (if disabled, will return zero); pointed |
| RSB_IO_WANT_MEM_ALLOC_TOT | Used for getting the total amount of memory allocated by librsb employing librsb's memory allocation wrapper (if disabled, will return zero); pointed |
| RSB_IO_WANT_LEAF_LEVEL_MULTIVEC | Specifies whether the default multi-vector ops shall act at a leaf level (default value of 0 is yes). Specified as a pointed integer (rsb_int_t) number, in {-1,[0]}. (internal) |
| RSB_IO_WANT_MAX_MEMORY_ALLOCATIONS | Specifies an upper limit to the count of allocated memory areas (default value of 0 means no limit). Specified as a pointed |
| RSB_IO_WANT_MAX_MEMORY_ALLOCATED | Specifies an upper limit to the amount of allocated memory (default value of 0 means no limit). Specified as a pointed |
| RSB_IO_WANT_LIBRSB_ETIME | Represents time spent in librsb. Specified as a pointed rsb_time_t. Only works if statistics collection ( |
| RSB_IO_WANT_VERBOSE_TUNING | Auto tuning verbosity level for rsb_tune_spmm/rsb_tune_spsm. If 0, no verbosity; if 1, verbose; if 2, verbose with trace files being dumped. |
Function Documentation
◆ rsb_coo_cleanup()
| rsb_err_t rsb_coo_cleanup | ( | rsb_coo_idx_t * | nnzp, |
| void * | VA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | IA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | JA, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | nnzA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | nrA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | ncA, | ||
| rsb_type_t | typecode, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flagsA | ||
| ) |
Compacts the given COO input arrays representing a sparse matrix  . Will either sum together duplicates or use the last one, depending on whether RSB_FLAG_DUPLICATES_KEEP_LAST or RSB_FLAG_DUPLICATES_SUM is present in flagsA.
. Will either sum together duplicates or use the last one, depending on whether RSB_FLAG_DUPLICATES_KEEP_LAST or RSB_FLAG_DUPLICATES_SUM is present in flagsA.
It is important that the input is sorted and flagsA shall contain RSB_FLAG_SORTED_INPUT, otherwise the algorithm's complexity will be quadratic.
- Parameters
-
nnzp Pointer to the number of nonzeroes after the cleanup. VA,IA,JA Output numerical values ( VA) array; output row (IA) and column (JA) indices arrays.nnzA The number of nonzeroes in the input arrays representing matrix  .
. nrA,ncA The number of rows and columns of the sparse matrix  .
. typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). flagsA A valid combination of matrix storage flags. If unsure, use RSB_FLAG_NOFLAGS.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- See also
- rsb_time, rsb_coo_sort
- rsb_coo_sort
- Warning
- This is an experimental librsb-1.3 function.
- Note
- By invoking with swapped
IAandJA(and swappingnrAandncAas well) one can obtain column major order.
Examples:
◆ rsb_coo_sort()
| rsb_err_t rsb_coo_sort | ( | void * | VA, |
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | IA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | JA, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | nnzA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | nrA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | ncA, | ||
| rsb_type_t | typecode, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flagsA | ||
| ) |
Sorts row-major the given COO input arrays representing a sparse matrix  .
.
- Parameters
-
VA,IA,JA Output numerical values ( VA) array; output row (IA) and column (JA) indices arrays.nnzA The number of nonzeroes in the input arrays representing matrix  .
. nrA,ncA The number of rows and columns of the sparse matrix  .
. typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). flagsA A valid combination of matrix storage flags. If unsure, use RSB_FLAG_NOFLAGS.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- See also
- rsb_time, rsb_coo_sort
- Note
- By invoking with swapped
IAandJA(and swappingnrAandncAas well) one can obtain column major order.
◆ rsb_file_mtx_get_dims()
| rsb_err_t rsb_file_mtx_get_dims | ( | const char * | filename, |
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | nrp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | ncp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | nzp, | ||
| rsb_flags_t * | flagsp | ||
| ) |
Reads structural information (dimensions, structural flags) for a matrix file into user specified (and optionally NULL) variables.
- Parameters
-
filename The specified matrix file name (cannot be NULL).nrp,ncp Output pointers to rows and columns count variables (can be NULL).nzp Output pointer to the nonzeroes count variable (can be NULL).flagsp Output pointer to the detected structural flags variable. Will be a combination of RSB_FLAG_LOWER, RSB_FLAG_UPPER, RSB_FLAG_SYMMETRIC, RSB_FLAG_HERMITIAN.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error. If read dimensions are illegal (see rsb_coo_idx_t,rsb_nnz_idx_t), RSB_ERR_LIMITS will be returned.
Example getting dimensions of a sparse matrix stored in a Matrix Market file:
- Note
- The only sparse matrix file format currently supported is Matrix Market. E.g.:
%%MatrixMarket matrix coordinate real symmetric % % A Hilbert Matrix of order 3, so with 3 rows, 3 columns, and 6 nonzeroes. % 3 3 6 1 1 1.0 2 1 0.5 2 2 0.33 3 1 0.33 3 2 0.25 3 3 0.2
In the above example header on the first line, you can specify eitherrealorcomplexorpatternfor the numerical type. Eithergeneral,symmetric,hermitiancan be specified for the structure. In case ofpatternmatrices, only coordinate indices will be loaded (savingpatternmatrices is not yet supported); in case ofrealmatrices, also one coefficient value will be saved/loaded; in the case ofcomplexmatrices, both the real and imaginary parts will be saved/loaded in addition to the indices. - Upper/lower flags will not be reported; hermitiannes do.
◆ rsb_file_mtx_load()
| struct rsb_mtx_t* rsb_file_mtx_load | ( | const rsb_char_t * | filename, |
| rsb_flags_t | flagsA, | ||
| rsb_type_t | typecode, | ||
| rsb_err_t * | errvalp | ||
| ) |
Loads a sparse matrix from the specified matrix file, assembling it in the format specified by flags, using the numerical type representation as specified by the user. Extra input errors or warnings verbosity can be enabled via the ./configure –enable-internals-error-verbosity option.
- Parameters
-
filename The specified matrix file name (cannot be NULL).flagsA A valid combination of matrix storage flags. typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). errvalp An optional (can be NULL) pointer to rsb_err_t where the error status will be written to.
- Returns
- On success, a valid pointer (
structrsb_mtx_t*) to the newly allocated matrix structure; on error,NULL.
- Note
- The only sparse matrix file format currently supported is Matrix Market. E.g.:
%%MatrixMarket matrix coordinate real symmetric % % A Hilbert Matrix of order 3, so with 3 rows, 3 columns, and 6 nonzeroes. % 3 3 6 1 1 1.0 2 1 0.5 2 2 0.33 3 1 0.33 3 2 0.25 3 3 0.2
In the above example header on the first line, you can specify eitherrealorcomplexorpatternfor the numerical type. Eithergeneral,symmetric,hermitiancan be specified for the structure. In case ofpatternmatrices, only coordinate indices will be loaded (savingpatternmatrices is not yet supported); in case ofrealmatrices, also one coefficient value will be saved/loaded; in the case ofcomplexmatrices, both the real and imaginary parts will be saved/loaded in addition to the indices.
Example loading a matrix from a Matrix Market file:
◆ rsb_file_mtx_rndr()
| rsb_err_t rsb_file_mtx_rndr | ( | void * | pmp, |
| const char * | filename, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | pmlWidth, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | pmWidth, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | pmHeight, | ||
| rsb_marf_t | rflags | ||
| ) |
Renders as pixel map the matrix contained in a matrix file.
- Parameters
-
pmp Pixel map array pointer. filename The specified matrix file name (cannot be NULL).pmlWidth stride between lines (in pixels; no less than pmWidth).pmWidth Pixel map width (in pixels or points). pmHeight Pixel map height (in pixels or points). rflags The color mode; only RSB_MARF_RGB is supported for now (1 byte per channel, 3 channels — red, green, blue): this requires array pmpto be at least (3*pmlWidth*bytes large.pmHeight)
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- Note
- At the time being,
pmlWidthis required to be equal topmWidth.
Example rendering a matrix from a Matrix Market file to a pixelmap in memory:
- See also
- rsb_mtx_rndr, rsb_file_mtx_rndr
◆ rsb_file_mtx_save()
| rsb_err_t rsb_file_mtx_save | ( | const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, |
| const rsb_char_t * | filename | ||
| ) |
Saves the given matrix to the specified matrix file.
- Parameters
-
mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. filename The specified output file name (if NULL, will write to standard output).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- Warning
- Some structural info contained in the matrix structural flags may be lost in the output data.
- Note
- The only sparse matrix file format currently supported is Matrix Market. E.g.:
%%MatrixMarket matrix coordinate real symmetric % % A Hilbert Matrix of order 3, so with 3 rows, 3 columns, and 6 nonzeroes. % 3 3 6 1 1 1.0 2 1 0.5 2 2 0.33 3 1 0.33 3 2 0.25 3 3 0.2
In the above example header on the first line, you can specify eitherrealorcomplexorpatternfor the numerical type. Eithergeneral,symmetric,hermitiancan be specified for the structure. In case ofpatternmatrices, only coordinate indices will be loaded (savingpatternmatrices is not yet supported); in case ofrealmatrices, also one coefficient value will be saved/loaded; in the case ofcomplexmatrices, both the real and imaginary parts will be saved/loaded in addition to the indices.
Example, printing a matrix to standard output:
◆ rsb_file_vec_load()
| rsb_err_t rsb_file_vec_load | ( | const rsb_char_t * | filename, |
| rsb_type_t | typecode, | ||
| void * | Yp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | yvlp | ||
| ) |
Loads a dense vector from the specified file, using the numerical type representation as specified by the user. This function is intended to be called in two steps: first with Yp=NULL, in order to write the vector length to *yvlp ; then, with yvlp=NULL, to get Yp written.
- Parameters
-
filename The specified vector file name (cannot be NULL).typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). Yp The input array vector. yvlp An optional pointer (can be NULL). If supplied, vector length will be written here, and no vector will be read.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
Example loading vector matrix from file
- Note
- The only dense vector file format currently supported is Matrix Market. E.g.:
%%MatrixMarket matrix array complex general % Test MatrixMarket file with a complex vector. % Note: a blank line like the following is OK. 6 1 11.000000000000000E+000 12.000000000000000E+000 21.000000000000000E+000 22.000000000000000E+000 31.000000000000000E+000 32.000000000000000E+000 41.000000000000000E+000 42.000000000000000E+000 51.000000000000000E+000 52.000000000000000E+000 61.000000000000000E+000 62.000000000000000E+000
In the above example header on the first line, you can specify eitherrealorcomplexorpatternfor the numerical type.
◆ rsb_file_vec_save()
| rsb_err_t rsb_file_vec_save | ( | const rsb_char_t * | filename, |
| rsb_type_t | typecode, | ||
| const void * | Yp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | yvl | ||
| ) |
Saves a dense vector to the specified file, using the numerical type representation as specified by the user. This function assumes Yp!=NULL and yvl>0.
- Parameters
-
filename The specified vector file name (cannot be NULL).typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). Yp The output array vector. yvl Output vector length.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- Note
- The only dense vector file format currently supported is Matrix Market. E.g.:
%%MatrixMarket matrix array complex general % Test MatrixMarket file with a complex vector. % Note: a blank line like the following is OK. 6 1 11.000000000000000E+000 12.000000000000000E+000 21.000000000000000E+000 22.000000000000000E+000 31.000000000000000E+000 32.000000000000000E+000 41.000000000000000E+000 42.000000000000000E+000 51.000000000000000E+000 52.000000000000000E+000 61.000000000000000E+000 62.000000000000000E+000
In the above example header on the first line, you can specify eitherrealorcomplexorpatternfor the numerical type.
Example printing to standard output:
◆ rsb_lib_exit()
| rsb_err_t rsb_lib_exit | ( | struct rsb_initopts * | iop | ) |
Finalize librsb.
rsb_lib_exit should be called after having freed all matrices.
If not all of the data structures were properly deallocated before, this function may still attempt finalizing the library and return the RSB_ERR_MEMORY_LEAK error code (this depends on the –enable-allocator-wrapper configure time option). Any allocated memory will be lost (librsb does not keep track of allocated matrices).
Internal library state will be cleared. After this call, it is legal to initialize the library again, by calling rsb_lib_init().
On an error, the library state may be inconsistent, so it is advisable to either terminate program execution (rather than forcing a new initialization with rsb_lib_init()).
Parameter iop is reserved for future use; for now it is safe to pass RSB_NULL_EXIT_OPTIONS.
It should be safe to call rsb_lib_exit() more than once.
- Parameters
-
iop A pointer to a rsb_initopts structure with library options. It may be NULL(or better, RSB_NULL_INIT_OPTIONS/RSB_NULL_EXIT_OPTIONS) for specifying default options.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
An example snippet declaring an error variable accumulator at program's beginning:
and finalizing the library at program's end:
- See also
- rsb_lib_init, rsb_lib_set_opt_str, rsb_lib_reinit, rsb_lib_exit, rsb_lib_get_opt, rsb_lib_set_opt, or (deprecated) macros RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_GET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_SET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_C_IOP..
◆ rsb_lib_get_opt()
Gets value of a library option.
A value specified by the request flag iof will be fetched from the library internal state and *iop will be updated accordingly.
- Parameters
-
iof library options flags. See rsb_opt_t for a list of valid options. iop library options value output pointer (pointed location will be updated).
- See also
- RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_GET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_SET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_C_IOP
- rsb_lib_init, rsb_lib_set_opt_str, rsb_lib_reinit, rsb_lib_exit, rsb_lib_get_opt, rsb_lib_set_opt, or (deprecated) macros RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_GET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_SET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_C_IOP..
◆ rsb_lib_init()
| rsb_err_t rsb_lib_init | ( | struct rsb_initopts * | iop | ) |
This is the library initialization function.
It must be called only once before using any other library function.
It is allowed to call it again after rsb_lib_exit().
To fine-tune the library behaviour, one may specify a number of options via the iop parameter.
Options may be specified also after rsb_lib_init() by calling rsb_lib_reinit().
One may call RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_GET with flag RSB_IO_WANT_IS_INITIALIZED_MARKER to verify whether the library has been initialized or not.
If the RSB_NUM_THREADS environment variable is set, rsb_lib_init() uses it and sets the number of active threads, thus overriding what detected by the OpenMP runtime (e.g. OMP_NUM_THREADS).
- Parameters
-
iop A pointer to a rsb_initopts structure with library options. It may be NULL(or better, RSB_NULL_INIT_OPTIONS/RSB_NULL_EXIT_OPTIONS) for specifying default options.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
An example snippet declaring an error variable accumulator at program's beginning:
and initializing the library soon thereafter:
- See also
- rsb_lib_init, rsb_lib_set_opt_str, rsb_lib_reinit, rsb_lib_exit, rsb_lib_get_opt, rsb_lib_set_opt, or (deprecated) macros RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_GET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_SET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_C_IOP..
◆ rsb_lib_reinit()
| rsb_err_t rsb_lib_reinit | ( | struct rsb_initopts * | iop | ) |
Changes the library operation options which were set at initialization time either by a user or as defaults.
Not all options may be supported, depending on build time library settings.
If an unsupported option was specified, an appropriate error (e.g.: RSB_ERR_UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION) will be returned.
On the first error, option processing is interrupted and the remaining options (if any) are not processed.
Program execution may continue safely even if an error code is returned (that is, library status should be consistent).
- Parameters
-
iop A pointer to a rsb_initopts structure with library options. It may be NULL(or better, RSB_NULL_INIT_OPTIONS/RSB_NULL_EXIT_OPTIONS) for specifying default options.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- See also
- rsb_lib_init, rsb_lib_set_opt_str, rsb_lib_reinit, rsb_lib_exit, rsb_lib_get_opt, rsb_lib_set_opt, or (deprecated) macros RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_GET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_SET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_C_IOP..
◆ rsb_lib_set_opt()
Sets value of a library option.
A value specified by the request flag iof will be fetched from *iop and will be used to update the selected option in the library internal state.
- Parameters
-
iof library options flags. See rsb_opt_t for a list of valid options. iop library options value output pointer (pointed location will be updated).
Example snip:
- See also
- RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_GET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_SET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_C_IOP
- rsb_lib_init, rsb_lib_set_opt_str, rsb_lib_reinit, rsb_lib_exit, rsb_lib_get_opt, rsb_lib_set_opt, or (deprecated) macros RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_GET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_SET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_C_IOP..
◆ rsb_lib_set_opt_str()
| rsb_err_t rsb_lib_set_opt_str | ( | const rsb_char_t * | opnp, |
| const rsb_char_t * | opvp | ||
| ) |
Specifies individual library options in order to fine-tune the library behaviour.
Both the option name and the value shall be expressed as strings, identical to their preprocessor identifiers (see rsb_opt_t ). The opnp string will be translated internally to the corresponding request flag values, and the passed value will be parsed out of the opvp string.
- Parameters
-
opnp A pointer to a library option input name string (may not be NULL).opvp A pointer to a library option input value string (may not be NULL).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- See also
- rsb_lib_init, rsb_lib_set_opt_str, rsb_lib_reinit, rsb_lib_exit, rsb_lib_get_opt, rsb_lib_set_opt, or (deprecated) macros RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_GET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_SET, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE, RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_C_IOP..
◆ rsb_mtx_add_to_dense()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_add_to_dense | ( | const void * | alphap, |
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | ldB, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | nrB, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | ncB, | ||
| rsb_bool_t | rowmajorB, | ||
| void * | Bp | ||
| ) |
Dense matrix B is updated by adding scaled sparse matrix 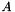 to it:
to it: 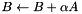
- Parameters
-
alphap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value (of the same type as matrix).mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. ldB Leading dimension of Bparray.nrB,ncB The number of rows and columns for the dense matrix 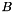 .
. rowmajorB RSB_BOOL_TRUE if the dense matrix 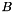 is considered stored as row major, or RSB_BOOL_FALSE if as column major.
is considered stored as row major, or RSB_BOOL_FALSE if as column major. Bp Array representing the dense matrix 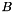 .
.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
Example snip:
- Note
- Please note that it suffices to 'transpose'
Bp'sdescription parameters to get transposed summed in.
transposed summed in. - Symmetry is currently not expanded.
- Threaded, for large enough matrices.
- See also
- rsb_spmsp_to_dense, rsb_sppsp, rsb_spmsp, rsb_mtx_add_to_dense
◆ rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_begin()
| struct rsb_mtx_t* rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_begin | ( | rsb_nnz_idx_t | nnzA, |
| rsb_type_t | typecode, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | nrA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | ncA, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flagsA, | ||
| rsb_err_t * | errvalp | ||
| ) |
Creates an empty matrix structure in assembly state. The user then populates it using rsb_mtx_set_vals() repeatedly; then assembles it with rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_end().
- Parameters
-
nnzA A rough estimate of the number of nonzeroes matrix  will host (used for optimizing arrays allocation). If you do not know yet, you can specify zero.
will host (used for optimizing arrays allocation). If you do not know yet, you can specify zero. typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). nrA,ncA The number of rows and columns of the sparse matrix  .
. flagsA A valid combination of index conversion and matrix storage flags and other meaningful flags. The encouraged base choice here is RSB_FLAG_DEFAULT_RSB_MATRIX_FLAGS. If Fortran (1 based) indices are being used for the IA, JA arrays, then the RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE flag should be added. If symmetric storage is desired, then RSB_FLAG_SYMMETRIC (or RSB_FLAG_HERMITIAN, for Hermitian matrices) is necessary, in combination with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER or RSB_FLAG_UPPER. If you intend to use this matrix for triangular solution (e.g.: rsb_spsv()/rsb_spsm()), it needs to be triangular and specified with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR or RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR, and not have RSB_FLAG_LOWER_SYMMETRIC or RSB_FLAG_LOWER_HERMITIAN. Nonzeroes non complying with the specified flags will be ignored. If a matrix is both RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR and RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR at the same time, then it's diagonal, for which shorthand: RSB_FLAG_DIAGONAL can be used. If RSB_FLAG_UNIT_DIAG_IMPLICIT is present, diagonal entries will be not represented but assumed to be unitary. If RSB_FLAG_DUPLICATES_SUM is present, duplicate entries will be summed together. If RSB_FLAG_DISCARD_ZEROS is present, zeroes will be discarded. errvalp An optional (can be NULL) pointer to rsb_err_t where the error status will be written to.
- Returns
- Pointer to a
rsb_mtx_tmatrix structure in assembly state, orNULL(on error).
- Warning
- This function has not been thoroughly tested.
◆ rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_const()
| struct rsb_mtx_t* rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_const | ( | const void * | VA, |
| const rsb_coo_idx_t * | IA, | ||
| const rsb_coo_idx_t * | JA, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | nnzA, | ||
| rsb_type_t | typecode, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | nrA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | ncA, | ||
| rsb_blk_idx_t | brA, | ||
| rsb_blk_idx_t | bcA, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flagsA, | ||
| rsb_err_t * | errvalp | ||
| ) |
Given as input COO arrays VA,IA,JA, allocates and assembles an RSB matrix using separate arrays.
- Parameters
-
VA,IA,JA Input numerical values ( VA) array; row (IA) and column (JA) input indices arrays.nnzA The number of nonzeroes in the input arrays representing matrix  .
. typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). nrA,ncA The number of rows and columns of the sparse matrix  . If any of nrA or ncA is zero, it will be detected on the basis of the
. If any of nrA or ncA is zero, it will be detected on the basis of the IAandJAarrays and flagsA.brA,bcA Blocking parameters: brAshould be set to 1 or RSB_DEFAULT_ROW_BLOCKING (currently unused, reserved for future use);bcAshould be set to 1 or RSB_DEFAULT_ROW_BLOCKING (currently unused, reserved for future use).flagsA A valid combination of index conversion and matrix storage flags and other meaningful flags. The encouraged base choice here is RSB_FLAG_DEFAULT_RSB_MATRIX_FLAGS. If Fortran (1 based) indices are being used for the IA, JA arrays, then the RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE flag should be added. If symmetric storage is desired, then RSB_FLAG_SYMMETRIC (or RSB_FLAG_HERMITIAN, for Hermitian matrices) is necessary, in combination with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER or RSB_FLAG_UPPER. If you intend to use this matrix for triangular solution (e.g.: rsb_spsv()/rsb_spsm()), it needs to be triangular and specified with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR or RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR, and not have RSB_FLAG_LOWER_SYMMETRIC or RSB_FLAG_LOWER_HERMITIAN. Nonzeroes non complying with the specified flags will be ignored. If a matrix is both RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR and RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR at the same time, then it's diagonal, for which shorthand: RSB_FLAG_DIAGONAL can be used. If RSB_FLAG_UNIT_DIAG_IMPLICIT is present, diagonal entries will be not represented but assumed to be unitary. If RSB_FLAG_DUPLICATES_SUM is present, duplicate entries will be summed together. If RSB_FLAG_DISCARD_ZEROS is present, zeroes will be discarded. errvalp An optional (can be NULL) pointer to rsb_err_t where the error status will be written to.
- Returns
- On success, a valid pointer (
structrsb_mtx_t*) to the newly allocated matrix structure; on error,NULL.
Example snip:
And another, with duplicate sum flags:
And yet another, allocating a triangular matrix:
◆ rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_end()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_end | ( | struct rsb_mtx_t ** | mtxApp | ) |
Assembles RSB arrays for a matrix in build state created with rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_begin() and populated with rsb_mtx_set_vals().
After assembly, any operation on the matrix is allowed.
- Parameters
-
mtxApp rsb_mtx_tpointer to an unassembled matrix address.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- Warning
- This function has not been thoroughly tested.
- Note
- Note that the memory location of the matrix will be changed by this call, and the (old)
*mtxAppaddress value will be not valid anymore.
◆ rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_inplace()
| struct rsb_mtx_t* rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_inplace | ( | void * | VA, |
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | IA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | JA, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | nnzA, | ||
| rsb_type_t | typecode, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | nrA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | ncA, | ||
| rsb_blk_idx_t | brA, | ||
| rsb_blk_idx_t | bcA, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flagsA, | ||
| rsb_err_t * | errvalp | ||
| ) |
Given as input COO arrays VA,IA,JA, allocates and assembles an RSB matrix reusing input arrays.
Assumes all three VA,IA,JA arrays are at least max(nnzA,nrA+1,ncA+1) sized. The user is expected NOT to use these arrays until the matrix has been destroyed with rsb_mtx_free(). Then, it is possible to use these arrays again.
- Parameters
-
VA,IA,JA Input/output numerical values array ( VA); row (IA) and column (JA) indices arrays.nnzA The number of nonzeroes in the input arrays representing matrix  .
. typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). nrA,ncA The number of rows and columns of the sparse matrix  .
. brA,bcA Blocking parameters: brAshould be set to 1 or RSB_DEFAULT_ROW_BLOCKING (currently unused, reserved for future use);bcAshould be set to 1 or RSB_DEFAULT_ROW_BLOCKING (currently unused, reserved for future use).flagsA A valid combination of index conversion and matrix storage flags and other meaningful flags. The encouraged base choice here is RSB_FLAG_DEFAULT_RSB_MATRIX_FLAGS. If Fortran (1 based) indices are being used for the IA, JA arrays, then the RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE flag should be added. If symmetric storage is desired, then RSB_FLAG_SYMMETRIC (or RSB_FLAG_HERMITIAN, for Hermitian matrices) is necessary, in combination with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER or RSB_FLAG_UPPER. If you intend to use this matrix for triangular solution (e.g.: rsb_spsv()/rsb_spsm()), it needs to be triangular and specified with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR or RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR, and not have RSB_FLAG_LOWER_SYMMETRIC or RSB_FLAG_LOWER_HERMITIAN. Nonzeroes non complying with the specified flags will be ignored. If a matrix is both RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR and RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR at the same time, then it's diagonal, for which shorthand: RSB_FLAG_DIAGONAL can be used. If RSB_FLAG_UNIT_DIAG_IMPLICIT is present, diagonal entries will be not represented but assumed to be unitary. If RSB_FLAG_DUPLICATES_SUM is present, duplicate entries will be summed together. If RSB_FLAG_DISCARD_ZEROS is present, zeroes will be discarded. errvalp An optional (can be NULL) pointer to rsb_err_t where the error status will be written to.
- Returns
- On success, a valid pointer (
structrsb_mtx_t*) to the newly allocated matrix structure; on error,NULL.
◆ rsb_mtx_alloc_from_csc_const()
| struct rsb_mtx_t* rsb_mtx_alloc_from_csc_const | ( | const void * | VA, |
| const rsb_coo_idx_t * | IA, | ||
| const rsb_coo_idx_t * | CP, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | nnzA, | ||
| rsb_type_t | typecode, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | nrA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | ncA, | ||
| rsb_blk_idx_t | brA, | ||
| rsb_blk_idx_t | bcA, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flagsA, | ||
| rsb_err_t * | errvalp | ||
| ) |
Given input read only CSC format arrays, allocates and assembles an RSB matrix (stored in separate arrays).
- Parameters
-
VA,IA,CP Input numerical values ( VA) array, input row indices (IA) and compressed column (CP) indices arrays.nnzA The number of nonzeroes in the input arrays representing matrix  .
. typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). nrA,ncA The number of rows and columns of the sparse matrix  .
. brA,bcA Blocking parameters: brAshould be set to 1 or RSB_DEFAULT_ROW_BLOCKING (currently unused, reserved for future use);bcAshould be set to 1 or RSB_DEFAULT_ROW_BLOCKING (currently unused, reserved for future use).flagsA A valid combination of index conversion and matrix storage flags and other meaningful flags. The encouraged base choice here is RSB_FLAG_DEFAULT_RSB_MATRIX_FLAGS. If Fortran (1 based) indices are being used for the IA, JA arrays, then the RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE flag should be added. If symmetric storage is desired, then RSB_FLAG_SYMMETRIC (or RSB_FLAG_HERMITIAN, for Hermitian matrices) is necessary, in combination with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER or RSB_FLAG_UPPER. If you intend to use this matrix for triangular solution (e.g.: rsb_spsv()/rsb_spsm()), it needs to be triangular and specified with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR or RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR, and not have RSB_FLAG_LOWER_SYMMETRIC or RSB_FLAG_LOWER_HERMITIAN. Nonzeroes non complying with the specified flags will be ignored. If a matrix is both RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR and RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR at the same time, then it's diagonal, for which shorthand: RSB_FLAG_DIAGONAL can be used. If RSB_FLAG_UNIT_DIAG_IMPLICIT is present, diagonal entries will be not represented but assumed to be unitary. If RSB_FLAG_DUPLICATES_SUM is present, duplicate entries will be summed together. If RSB_FLAG_DISCARD_ZEROS is present, zeroes will be discarded. errvalp An optional (can be NULL) pointer to rsb_err_t where the error status will be written to.
- Returns
- On success, a valid pointer (
structrsb_mtx_t*) to the newly allocated matrix structure; on error,NULL.
- See also
- rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_const, rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_inplace, rsb_mtx_free, rsb_mtx_clone, rsb_mtx_alloc_from_csr_const, rsb_mtx_alloc_from_csc_const, rsb_mtx_alloc_from_csr_inplace, rsb_mtx_switch_to_csr, rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_begin, rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_end
Example:
◆ rsb_mtx_alloc_from_csr_const()
| struct rsb_mtx_t* rsb_mtx_alloc_from_csr_const | ( | const void * | VA, |
| const rsb_coo_idx_t * | RP, | ||
| const rsb_coo_idx_t * | JA, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | nnzA, | ||
| rsb_type_t | typecode, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | nrA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | ncA, | ||
| rsb_blk_idx_t | brA, | ||
| rsb_blk_idx_t | bcA, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flagsA, | ||
| rsb_err_t * | errvalp | ||
| ) |
Given input read only CSR format arrays, allocates and assembles an RSB matrix (stored in separate arrays).
- Parameters
-
VA,RP,JA Input numerical values ( VA) array; compressed rows (RP) and column (JA) input indices arrays.nnzA The number of nonzeroes in the input arrays representing matrix  .
. typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). nrA,ncA The number of rows and columns of the sparse matrix  .
. brA,bcA Blocking parameters: brAshould be set to 1 or RSB_DEFAULT_ROW_BLOCKING (currently unused, reserved for future use);bcAshould be set to 1 or RSB_DEFAULT_ROW_BLOCKING (currently unused, reserved for future use).flagsA A valid combination of index conversion and matrix storage flags and other meaningful flags. The encouraged base choice here is RSB_FLAG_DEFAULT_RSB_MATRIX_FLAGS. If Fortran (1 based) indices are being used for the IA, JA arrays, then the RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE flag should be added. If symmetric storage is desired, then RSB_FLAG_SYMMETRIC (or RSB_FLAG_HERMITIAN, for Hermitian matrices) is necessary, in combination with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER or RSB_FLAG_UPPER. If you intend to use this matrix for triangular solution (e.g.: rsb_spsv()/rsb_spsm()), it needs to be triangular and specified with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR or RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR, and not have RSB_FLAG_LOWER_SYMMETRIC or RSB_FLAG_LOWER_HERMITIAN. Nonzeroes non complying with the specified flags will be ignored. If a matrix is both RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR and RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR at the same time, then it's diagonal, for which shorthand: RSB_FLAG_DIAGONAL can be used. If RSB_FLAG_UNIT_DIAG_IMPLICIT is present, diagonal entries will be not represented but assumed to be unitary. If RSB_FLAG_DUPLICATES_SUM is present, duplicate entries will be summed together. If RSB_FLAG_DISCARD_ZEROS is present, zeroes will be discarded. errvalp An optional (can be NULL) pointer to rsb_err_t where the error status will be written to.
- Returns
- On success, a valid pointer (
structrsb_mtx_t*) to the newly allocated matrix structure; on error,NULL.
◆ rsb_mtx_alloc_from_csr_inplace()
| struct rsb_mtx_t* rsb_mtx_alloc_from_csr_inplace | ( | void * | VA, |
| rsb_nnz_idx_t * | RP, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | JA, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | nnzA, | ||
| rsb_type_t | typecode, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | nrA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | ncA, | ||
| rsb_blk_idx_t | brA, | ||
| rsb_blk_idx_t | bcA, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flagsA, | ||
| rsb_err_t * | errvalp | ||
| ) |
Given as input CSR arrays VA,RP,JA , allocates and assembles an RSB matrix reusing input arrays.
Assumes all three VA,IA,JA arrays are at least max(nnzA,nrA+1,ncA+1) sized. The user is expected NOT to use these arrays until the matrix has been destroyed with rsb_mtx_free(). Then, it is possible to use these arrays again.
- Parameters
-
VA,RP,JA Input numerical values ( VA) array; compressed rows (RP) and column (JA) input indices arrays. Will not be freed by rsb_mtx_free().nnzA The number of nonzeroes in the input arrays representing matrix  .
. typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). nrA,ncA The number of rows and columns of the sparse matrix  .
. brA,bcA Blocking parameters: brAshould be set to 1 or RSB_DEFAULT_ROW_BLOCKING (currently unused, reserved for future use);bcAshould be set to 1 or RSB_DEFAULT_ROW_BLOCKING (currently unused, reserved for future use).flagsA A valid combination of index conversion and matrix storage flags and other meaningful flags. The encouraged base choice here is RSB_FLAG_DEFAULT_RSB_MATRIX_FLAGS. If Fortran (1 based) indices are being used for the IA, JA arrays, then the RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE flag should be added. If symmetric storage is desired, then RSB_FLAG_SYMMETRIC (or RSB_FLAG_HERMITIAN, for Hermitian matrices) is necessary, in combination with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER or RSB_FLAG_UPPER. If you intend to use this matrix for triangular solution (e.g.: rsb_spsv()/rsb_spsm()), it needs to be triangular and specified with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR or RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR, and not have RSB_FLAG_LOWER_SYMMETRIC or RSB_FLAG_LOWER_HERMITIAN. Nonzeroes non complying with the specified flags will be ignored. If a matrix is both RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR and RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR at the same time, then it's diagonal, for which shorthand: RSB_FLAG_DIAGONAL can be used. If RSB_FLAG_UNIT_DIAG_IMPLICIT is present, diagonal entries will be not represented but assumed to be unitary. If RSB_FLAG_DUPLICATES_SUM is present, duplicate entries will be summed together. If RSB_FLAG_DISCARD_ZEROS is present, zeroes will be discarded. errvalp An optional (can be NULL) pointer to rsb_err_t where the error status will be written to.
- Returns
- On success, a valid pointer (
structrsb_mtx_t*) to the newly allocated matrix structure; on error,NULL.
◆ rsb_mtx_clone()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_clone | ( | struct rsb_mtx_t ** | mtxBpp, |
| rsb_type_t | typecode, | ||
| rsb_trans_t | transA, | ||
| const void * | alphap, | ||
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flags | ||
| ) |
This function clones a given matrix, allocating a fresh data structure or overwriting an existing one.
Target type (specified by typecode) can be different from that in the matrix. If alphap=NULL, the cloned matrix will not be scaled.
This new structure will be completely separated and independent from the original one.
Examples:
- Parameters
-
mtxBpp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to an address for matrix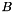 . If
. If *mtxBpp==NULL, a fresh clone will be assigned there; if not, the existing matrix structure will be freed and allocated to host the new one. The case*mtxBpp==mtxApis supported.typecode A valid type code for the desired output matrix (see matrix_type_symbols_section). transA Transposition parameter for  (see matrix_transposition_flags_section).
(see matrix_transposition_flags_section). alphap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value for scaling the output. Of the type code ofmtxAp.mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. flags Either RSB_FLAG_IDENTICAL_FLAGS or a combination of other flags, e.g.: RSB_FLAG_C_INDICES_INTERFACE, RSB_FLAG_SYMMETRIC, RSB_FLAG_HERMITIAN, RSB_FLAG_TRIANGULAR, RSB_FLAG_UPPER, RSB_FLAG_LOWER, RSB_FLAG_UNIT_DIAG_IMPLICIT, RSB_FLAG_DISCARD_ZEROS. Flag RSB_FLAG_EXTERNALLY_ALLOCATED_ARRAYS is forbidden. Flag RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE is ignored.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
Example snip:
◆ rsb_mtx_free()
| struct rsb_mtx_t* rsb_mtx_free | ( | struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp | ) |
Frees a previously allocated sparse matrix structure.
In the case the matrix has the RSB_FLAG_EXTERNALLY_ALLOCATED_ARRAYS flag, the main three data arrays VA,IA,JA will not be freed by rsb_mtx_free (see rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_inplace,rsb_mtx_alloc_from_csr_inplace).
- Parameters
-
mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation.
- Returns
- Always
NULL.
Example freeing a sparse matrix:
◆ rsb_mtx_get_coo()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_get_coo | ( | const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, |
| void * | VA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | IA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | JA, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flags | ||
| ) |
Returns the matrix converted in a coordinate storage format.
Elements will be stored in no particular order.
If there are structural or fill-in zero elements, these will be skipped.
Writes as many entries as there are nonzeroes (use rsb_mtx_get_info(mtxAp,RSB_MIF_MATRIX_NNZ__TO__RSB_NNZ_INDEX_T,&nnz)) to find out how many in order to allocate the arrays correctly.
- Parameters
-
mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. VA,IA,JA Output numerical values ( VA) array; output row (IA) and column (JA) indices arrays.flags Either RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE or RSB_FLAG_C_INDICES_INTERFACE (see flags_section flags section).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
◆ rsb_mtx_get_coo_block()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_get_coo_block | ( | const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, |
| void * | VA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | IA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | JA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | frA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | lrA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | fcA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | lcA, | ||
| const rsb_coo_idx_t * | IREN, | ||
| const rsb_coo_idx_t * | JREN, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t * | rnzp, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flags | ||
| ) |
Writes in COO format the specified submatrix.
Works in two stages: first the user invokes it with VA,IA,JA set to NULL to get *rnzp. Then the VA,IA,JA arrays can be allocated, and the function called again, this time with rnzp=NULL but the VA,IA,JA arrays pointers non NULL (or at least, one of them).
- Parameters
-
mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. VA,IA,JA Output numerical values ( VA) array; output row (IA) and column (JA) indices arrays.frA,lrA First and last row indices. fcA,lcA First and last column indices. IREN,JREN Renumbering arrays for IAandJA(respectively rows count and columns count sized). IfNULL, no renumbering will be used.rnzp A pointer where the number of relevant nonzero elements will be written to. flags Either RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE or RSB_FLAG_C_INDICES_INTERFACE (see flags_section flags section).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
Examples:
And other examples:
- Warning
- Expect this function to change soon (e.g.: have scaling parameters, etc.). Contact the author if you intend to use it.
◆ rsb_mtx_get_csr()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_get_csr | ( | rsb_type_t | typecode, |
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, | ||
| void * | VA, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t * | RP, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | JA, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flags | ||
| ) |
Fills the given arrays with the matrix expressed in the CSR format.
- Parameters
-
typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. VA,RP,JA Output numerical values ( VA) array, compressed row indices (RP) and column indices (JA) arrays.flags Either RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE or RSB_FLAG_C_INDICES_INTERFACE (see flags_section flags section).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
◆ rsb_mtx_get_info()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_get_info | ( | const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, |
| enum rsb_mif_t | miflags, | ||
| void * | minfop | ||
| ) |
Returns a specified matrix (numerical) property.
- Parameters
-
mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. miflags A valid value of matrix info flags (see rsb_mif_t for valid values). minfop Pointer to a variable of the right type, according to the matrix info flag specification (see rsb_mif_t).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
Example snip:
◆ rsb_mtx_get_info_str()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_get_info_str | ( | const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, |
| const rsb_char_t * | mis, | ||
| void * | minfop, | ||
| size_t | buflen | ||
| ) |
Returns a specified matrix (numerical) property, via a string form query.
- Parameters
-
mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. mis A string specifying any identifier among the matrix info ones. See rsb_mif_t for a list of valid identifiers that can be supplied in string form. minfop Pointer to a variable of the right type, according to the matrix info flag specification (see rsb_mif_t). buflen If greater than 0, minfopwill be treated as a string of lengthbuflenand filled with the desired value via the standardsnprintf()function.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
Example snip:
◆ rsb_mtx_get_nrm()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_get_nrm | ( | const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, |
| void * | Np, | ||
| enum rsb_extff_t | flags | ||
| ) |
Computes a matrix norm (either infinite-norm or or 2-norm or 1-norm).
- Parameters
-
mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. Np Points to a scalar value which will be overwritten with the selected norm. flags Either RSB_EXTF_NORM_ONE or RSB_EXTF_NORM_TWO or RSB_EXTF_NORM_INF.
In case of a complex type, only the real part will be written to Np.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
◆ rsb_mtx_get_prec()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_get_prec | ( | void * | opdp, |
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, | ||
| rsb_precf_t | prec_flags, | ||
| const void * | ipdp | ||
| ) |
A function computing a simple preconditioner out of mtxAp.
- Parameters
-
opdp Preconditioner data pointer (output). mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. prec_flags Valid preconditioner request flags (currently, only RSB_PRECF_ILU0 is supported; for it, *opdpwill be overwritten with tworsb_mtx_tpointers, respectively a lower and an upper matrix.).ipdp Preconditioner data pointer (input) (ignored at the moment).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
Example:
- Note
- Matrix should be square, have at least two rows, and have at least one nonzero.
◆ rsb_mtx_get_rows_sparse()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_get_rows_sparse | ( | rsb_trans_t | transA, |
| const void * | alphap, | ||
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, | ||
| void * | VA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | IA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t * | JA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | frA, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | lrA, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t * | rnzp, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flags | ||
| ) |
Writes to the given COO arrays the specified submatrix.
Invoke with VA,IA,JA set to NULL in order to get the nonzeroes count written to *rnzp, and know how large the arrays should be.
IA can be NULL (in this case it will be ignored). The written rows are ordered.
- Parameters
-
mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. VA,IA,JA Output numerical values ( VA) array; input row (IA) and column (JA) indices arrays.frA,lrA First and last row indices. rnzp A pointer where the number of relevant nonzero elements will be written to. alphap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value (of the same type as matrix).transA Transposition parameter for  (see matrix_transposition_flags_section).
(see matrix_transposition_flags_section). flags Either RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE or RSB_FLAG_C_INDICES_INTERFACE (see flags_section flags section).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
Example snip:
◆ rsb_mtx_get_vals()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_get_vals | ( | const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, |
| void * | VA, | ||
| const rsb_coo_idx_t * | IA, | ||
| const rsb_coo_idx_t * | JA, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | nnz, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flags | ||
| ) |
Gets the specified matrix elements, if found. Please note that unlike rsb_mtx_set_vals, the matrix has to be fully assembled here.
- Parameters
-
mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. VA,IA,JA Output numerical values ( VA) array; input row (IA) and column (JA) indices arrays.nnz The number of nonzeroes in the input arrays. flags Either RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE or RSB_FLAG_C_INDICES_INTERFACE (see flags_section flags section).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
Example snip:
◆ rsb_mtx_get_vec()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_get_vec | ( | const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, |
| void * | Dp, | ||
| enum rsb_extff_t | flags | ||
| ) |
Will overwrite a supplied array with a specific vector quantity.
- Parameters
-
mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. Dp A valid pointer to a numerical vector array 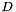 .
. flags Either one of the different extraction filter flags (e.g.: RSB_EXTF_DIAG, RSB_EXTF_SUMS_ROW, ...) .
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
◆ rsb_mtx_rndr()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_rndr | ( | const char * | filename, |
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | pmWidth, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | pmHeight, | ||
| rsb_marf_t | rflags | ||
| ) |
Renders a matrix to a file. Currently, only Encapsulated Postscript (EPS) is supported.
- Parameters
-
filename The specified output file name (if NULL, will write to standard output).mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. pmWidth Pixel map width (in pixels or points). pmHeight Pixel map height (in pixels or points). rflags The color mode; only RSB_MARF_RGB is supported for now (1 byte per channel, 3 channels — red, green, blue): this requires array pmpto be at least (3*pmlWidth*bytes large.pmHeight)
Example rendering a sparse matrix to Postscript:
Setting environment variable RSB_USE_HOSTNAME=0 prevents hostname being in the EPS plot internal comments.
- See also
- rsb_mtx_rndr, rsb_file_mtx_rndr
◆ rsb_mtx_set_vals()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_set_vals | ( | struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, |
| const void * | VA, | ||
| const rsb_coo_idx_t * | IA, | ||
| const rsb_coo_idx_t * | JA, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | nnz, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flags | ||
| ) |
Updates the specified matrix elements, if found in the nonzero pattern.
In the special case of a matrix in assembly state (that is, one that has been created as empty with rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_begin() and not yet assembled with rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_end() ) all the supplied matrix elements will be accepted: whether already present or not.
- Parameters
-
mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. VA,IA,JA Input numerical values ( VA) array; row (IA) and column (JA) input indices arrays.nnz The number of nonzeroes in the input arrays. flags Either RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE or RSB_FLAG_C_INDICES_INTERFACE plus either RSB_FLAG_DUPLICATES_SUM (to sum into) or RSB_FLAG_DUPLICATES_KEEP_LAST (to overwrite entries) (see flags_section flags section).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- See also
- rsb_mtx_upd_vals, rsb_mtx_set_vals
◆ rsb_mtx_switch_to_coo()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_switch_to_coo | ( | struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, |
| void ** | VAp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t ** | IAp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t ** | JAp, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flags | ||
| ) |
Switches a matrix to COO arrays in place.
- Parameters
-
mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. VAp,IAp,JAp Output numerical values ( VAp) array pointer; output row (IAp) and column (JAp) indices arrays pointers.flags A combination of RSB_FLAG_C_INDICES_INTERFACE, RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE, RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE. (see flags_section flags section).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- Note
- This function is only valid if
mtxAphas been assembled in place (that is, in the arrays that are being reclaimed), so with e.g.: rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_inplace(). Please also note that the matrix will get freed internally and somtxApwill not be usable in any way afterwards.
- Warning
- This function has not been thoroughly tested.
Example:
◆ rsb_mtx_switch_to_csr()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_switch_to_csr | ( | struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, |
| void ** | VAp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t ** | IAp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t ** | JAp, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | flags | ||
| ) |
Switches the matrix to the CSR format, in-place.
- Parameters
-
mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. VAp,IAp,JAp Output numerical values ( VAp) array pointer; output row (IAp) and column (JAp) indices arrays pointers.flags A valid combination of index conversion flags (that is, RSB_FLAG_C_INDICES_INTERFACE and RSB_FLAG_FORTRAN_INDICES_INTERFACE) and other meaningful flags. Symmetry flags shall be the same as in the matrix in use, because symmetry expansion may happen otherwise. Flags RSB_FLAG_EXTERNALLY_ALLOCATED_ARRAYS are forbidden.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- Note
- This function is only valid if
mtxAphas been assembled in place (that is, in the arrays that are being reclaimed), so with e.g.: rsb_mtx_alloc_from_coo_inplace(). Please also note that the matrix will get freed internally and somtxApwill not be usable in any way afterwards.
- Warning
- This function has not been thoroughly tested.
Example:
◆ rsb_mtx_upd_vals()
| rsb_err_t rsb_mtx_upd_vals | ( | struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, |
| enum rsb_elopf_t | elop_flags, | ||
| const void * | omegap | ||
| ) |
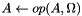 Updates the matrix
Updates the matrix  by applying either a row-wise or an elemental operation
by applying either a row-wise or an elemental operation 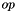 , which is determined by
, which is determined by elop_flags. If an unary operation is selected, omegap can be NULL.
- Parameters
-
mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. elop_flags Elemental operation specification flags (see rsb_elopf_t for valid choices). omegap Pointer to a numerical location(s) (of the same type as matrix).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
Example snip:
- See also
- rsb_mtx_upd_vals, rsb_mtx_set_vals
◆ rsb_perror()
Prints out to the specified stream a string corresponding to the error code (using <stdio.h>'s fprintf). If stream==NULL, will print out to the default output stream; see RSB_IO_WANT_OUTPUT_STREAM .
- Parameters
-
stream A (FILE*) pointer, as declared in<stdio.h>; can beNULL.errval A valid error flag value (see rsb_err_t).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- See also
- rsb_perror, rsb_strerror_r
◆ rsb_psblas_trans_to_rsb_trans()
| rsb_trans_t rsb_psblas_trans_to_rsb_trans | ( | const char | psbtrans | ) |
Translate a PSBLAS transposition value character to a librsb one.
See the PSBLAS library website/documentation for valid input values.
- Parameters
-
psbtrans Transposition parameter value valid in the PSBLAS library.
- Returns
- A valid transposition code; that is RSB_TRANSPOSITION_N for 'N', RSB_TRANSPOSITION_T for 'T', RSB_TRANSPOSITION_C for 'C', (See matrix_transposition_flags_section).
Example snip:
- See also
- rsb_psblas_trans_to_rsb_trans
◆ rsb_spmm()
| rsb_err_t rsb_spmm | ( | rsb_trans_t | transA, |
| const void * | alphap, | ||
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | nrhs, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | order, | ||
| const void * | Bp, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | ldB, | ||
| const void * | betap, | ||
| void * | Cp, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | ldC | ||
| ) |
Updates a dense matrix with the product of sparse matrix by dense matrix; that is, computes 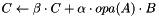 .
.
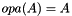 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_N; 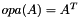 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_T; 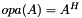 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_C; If –enable-rsb-num-threads has been specified at configure time, the RSB_NUM_THREADS environment variable will override the number of executing threads specified by OMP_NUM_THREADS. (See also RSB_IO_WANT_EXECUTING_THREADS). Setting order=RSB_FLAG_WANT_COLUMN_MAJOR_ORDER with ldC=0 and ldB=0 implies 'compact' defaults, that is no extra stride between the columns.
- Parameters
-
transA Transposition parameter for  (see matrix_transposition_flags_section).
(see matrix_transposition_flags_section). alphap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value (of the same type as matrix).mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. nrhs The number of right hand side vectors (cannot be <1).order A flag among RSB_FLAG_WANT_COLUMN_MAJOR_ORDER and RSB_FLAG_WANT_ROW_MAJOR_ORDER. For contiguous vector arrays, you probably want RSB_FLAG_WANT_COLUMN_MAJOR_ORDER. Bp The input vector array. ldB Leading dimension of Bparray.betap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value.Cp The output vector array. ldC Leading dimension of Cparray.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- Note
- Starting from version 1.3,
librsbuses C++ kernels for rsb_spmv/rsb_spmm. Assuming you configured–enable-debug-getenvs, you may set environment variableRSB_WANT_RSBPP=0to turn use the old C kernels.
- See also
- rsb_spmv, rsb_spmm, rsb_spata, rsb_tune_spmm
◆ rsb_spmsp()
| struct rsb_mtx_t* rsb_spmsp | ( | rsb_type_t | typecode, |
| rsb_trans_t | transA, | ||
| const void * | alphap, | ||
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, | ||
| rsb_trans_t | transB, | ||
| const void * | betap, | ||
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxBp, | ||
| rsb_err_t * | errvalp | ||
| ) |
Computes the weighted product of two sparse matrices in a new sparse matrix (also known as SpGEMM operation): 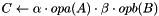 Symmetry/Hermitian flags are ignored by this operation.
Symmetry/Hermitian flags are ignored by this operation.
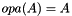 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_N; 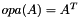 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_T; 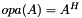 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_C; 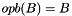 if
if transB=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_N; 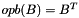 if
if transB=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_T; 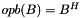 if
if transB=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_C;
- Parameters
-
typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). transA Transposition parameter for  (see matrix_transposition_flags_section).
(see matrix_transposition_flags_section). alphap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value (of the same type as matrix).mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. transB Transposition parameter for 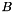 (see matrix_transposition_flags_section).
(see matrix_transposition_flags_section). betap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value.mtxBp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix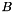 representation.
representation. errvalp An optional (can be NULL) pointer to rsb_err_t where the error status will be written to.
- Returns
- On success, a valid pointer (
structrsb_mtx_t*) to the newly allocated matrix structure; on error,NULL.
Example snip:
- Warning
- Parameters
alphap,betap,transA,transB are not yet taken in consideration. The following defaults are valid: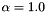 and
and 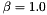 , and
, and transA=transB=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_N.
- See also
- rsb_spmsp_to_dense, rsb_sppsp, rsb_spmsp, rsb_mtx_add_to_dense
◆ rsb_spmsp_to_dense()
| rsb_err_t rsb_spmsp_to_dense | ( | rsb_type_t | typecode, |
| rsb_trans_t | transA, | ||
| const void * | alphap, | ||
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, | ||
| rsb_trans_t | transB, | ||
| const void * | betap, | ||
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxBp, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | ldC, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | nrC, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | ncC, | ||
| rsb_bool_t | rowmajorC, | ||
| void * | Cp | ||
| ) |
Computes the product of sparse matrices and adds it to a dense matrix: 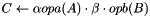 .
.
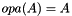 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_N; 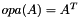 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_T; 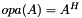 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_C; 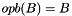 if
if transB=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_N; 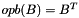 if
if transB=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_T; 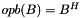 if
if transB=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_C;
- Parameters
-
typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). transA Transposition parameter for  (see matrix_transposition_flags_section).
(see matrix_transposition_flags_section). alphap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value (of the same type as matrix).mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. transB Transposition parameter for 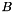 (see matrix_transposition_flags_section).
(see matrix_transposition_flags_section). betap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value.mtxBp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix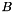 representation.
representation. ldC Leading dimension of Cparray.nrC,ncC The number of rows and columns for the dense matrix 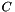 .
. rowmajorC RSB_BOOL_TRUE if the dense matrix 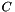 is considered stored as row major, or RSB_BOOL_FALSE if as column major.
is considered stored as row major, or RSB_BOOL_FALSE if as column major. Cp Array representing the dense matrix 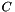 .
.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- Warning
- Parameters
alphap,betap,transA,transB are not yet taken in consideration. The following defaults are valid: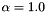 and
and 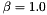 , and
, and transA=transB=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_N.
Example snip:
- See also
- rsb_spmsp_to_dense, rsb_sppsp, rsb_spmsp, rsb_mtx_add_to_dense
◆ rsb_spmv()
| rsb_err_t rsb_spmv | ( | rsb_trans_t | transA, |
| const void * | alphap, | ||
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, | ||
| const void * | Xp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | incX, | ||
| const void * | betap, | ||
| void * | Yp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | incY | ||
| ) |
Multiplies a sparse matrix 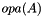 by a vector
by a vector 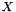 , updating vector
, updating vector 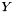 .
.
Computes 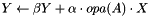 .
.
It is not allowed to supply same Xp and Yp (that is, Xp==Yp).
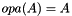 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_N; 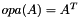 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_T; 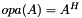 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_C; If –enable-rsb-num-threads has been specified at configure time, the RSB_NUM_THREADS environment variable will override the number of executing threads specified by OMP_NUM_THREADS. (See also RSB_IO_WANT_EXECUTING_THREADS).
- Parameters
-
transA Transposition parameter for  (see matrix_transposition_flags_section).
(see matrix_transposition_flags_section). alphap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value (of the same type as matrix).mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. Xp The input vector array. incX Spacing of vector elements in each input vector array (>=1). betap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value.Yp The output array vector. incY Spacing of vector elements in each output vector array (>=1).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
Example snip:
- Note
- Starting from version 1.3,
librsbuses C++ kernels for rsb_spmv/rsb_spmm. Assuming you configured–enable-debug-getenvs, you may set environment variableRSB_WANT_RSBPP=0to turn use the old C kernels.
- See also
- rsb_spmv, rsb_spmm, rsb_spata, rsb_tune_spmm
◆ rsb_sppsp()
| struct rsb_mtx_t* rsb_sppsp | ( | rsb_type_t | typecode, |
| rsb_trans_t | transA, | ||
| const void * | alphap, | ||
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, | ||
| rsb_trans_t | transB, | ||
| const void * | betap, | ||
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxBp, | ||
| rsb_err_t * | errvalp | ||
| ) |
Computes the weighted sum of two sparse matrices, returning a new matrix: 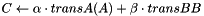 Symmetry flags are ignored in this operation.
Symmetry flags are ignored in this operation.
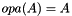 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_N; 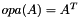 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_T; 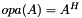 if
if transA=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_C; 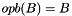 if
if transB=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_N; 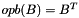 if
if transB=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_T; 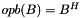 if
if transB=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_C;
- Parameters
-
typecode A valid type code for the given (numerical array) input pointer (see matrix_type_symbols_section). transA Transposition parameter for  (see matrix_transposition_flags_section).
(see matrix_transposition_flags_section). alphap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value (of the same type as matrix).mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. transB Transposition parameter for 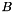 (see matrix_transposition_flags_section).
(see matrix_transposition_flags_section). betap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value.mtxBp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix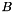 representation.
representation. errvalp An optional (can be NULL) pointer to rsb_err_t where the error status will be written to.
- Returns
- On success, a valid pointer (
structrsb_mtx_t*) to the newly allocated matrix structure; on error,NULL.
Example snip:
- See also
- rsb_spmsp_to_dense, rsb_sppsp, rsb_spmsp, rsb_mtx_add_to_dense
- Warning
- This function has not been thoroughly tested.
- This function is not optimized.
◆ rsb_spsm()
| rsb_err_t rsb_spsm | ( | rsb_trans_t | transT, |
| const void * | alphap, | ||
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxTp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | nrhs, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | order, | ||
| const void * | betap, | ||
| const void * | Bp, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | ldB, | ||
| void * | Cp, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | ldC | ||
| ) |
Computes 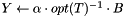 , with upper or lower triangular
, with upper or lower triangular 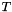 .
.
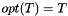 if
if transT=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_N; 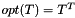 if
if transT=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_T; 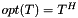 if
if transT=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_C;
- Parameters
-
transT Transposition parameter for 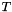 (see matrix_transposition_flags_section).
(see matrix_transposition_flags_section). alphap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value (of the same type as matrix).mtxTp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix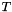 representation. The matrix must be triangular; that is, it must have been allocated with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR or RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR flags.
representation. The matrix must be triangular; that is, it must have been allocated with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR or RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR flags. nrhs The number of right hand side vectors (cannot be <1).order A flag among RSB_FLAG_WANT_COLUMN_MAJOR_ORDER and RSB_FLAG_WANT_ROW_MAJOR_ORDER. For contiguous vector arrays, you probably want RSB_FLAG_WANT_COLUMN_MAJOR_ORDER. betap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value.Bp The input vector array. ldB Leading dimension of Bparray.Cp The output vector array. ldC Leading dimension of Cparray.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
- See also
- rsb_spsm, rsb_spsv, rsb_tune_spsm
◆ rsb_spsv()
| rsb_err_t rsb_spsv | ( | rsb_trans_t | transT, |
| const void * | alphap, | ||
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxTp, | ||
| const void * | Xp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | incX, | ||
| void * | Yp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | incY | ||
| ) |
Computes 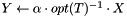 , with upper or lower triangular
, with upper or lower triangular  . It is allowed to supply same
. It is allowed to supply same Xp and Yp (that is, Xp==Yp).
 if
if transT=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_N; 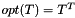 if
if transT=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_T; 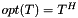 if
if transT=RSB_TRANSPOSITION_C;
- Parameters
-
transT Transposition parameter for  (see matrix_transposition_flags_section).
(see matrix_transposition_flags_section). alphap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value (of the same type as matrix).mtxTp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation. The matrix must be triangular; that is, it must have been allocated with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR or RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR flags.
representation. The matrix must be triangular; that is, it must have been allocated with either RSB_FLAG_LOWER_TRIANGULAR or RSB_FLAG_UPPER_TRIANGULAR flags. Xp The input vector array. incX Spacing of vector elements in each input vector array (>=1). Yp The output array vector. incY Spacing of vector elements in each output vector array (>=1).
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error. If
–enable-zero-division-checks-on-solvewas specified at configure time, attempts to solve a triangular matrix with zeroes on a diagonal will fail.
Example backsolving a triangular system:
- See also
- rsb_spsm, rsb_spsv, rsb_tune_spsm
◆ rsb_strerror_r()
| rsb_err_t rsb_strerror_r | ( | rsb_err_t | errval, |
| rsb_char_t * | buf, | ||
| size_t | buflen | ||
| ) |
Writes a textual description of an error code in the specified string buffer. No more than buflen characters will be written (comprehensive of the terminating NUL character).
- Parameters
-
errval A valid error flag value (see rsb_err_t). buf A valid string buffer pointer where to write to. buflen The string buffer length.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
Examples:
or
- See also
- rsb_perror, rsb_strerror_r
◆ rsb_time()
| rsb_time_t rsb_time | ( | void | ) |
Returns the current time in seconds. This function is meant to be used for computing wall clock time intervals (e.g.: for benchmarking purposes). The user should not rely on this function for absolute time computations.
- Returns
- A value for the current time, in seconds.
- See also
- rsb_time, rsb_coo_sort
◆ rsb_tune_spmm()
| rsb_err_t rsb_tune_spmm | ( | struct rsb_mtx_t ** | mtxOpp, |
| rsb_real_t * | sfp, | ||
| rsb_int_t * | tnp, | ||
| rsb_int_t | maxr, | ||
| rsb_time_t | maxt, | ||
| rsb_trans_t | transA, | ||
| const void * | alphap, | ||
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | nrhs, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | order, | ||
| const void * | Bp, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | ldB, | ||
| const void * | betap, | ||
| void * | Cp, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | ldC | ||
| ) |
An auto-tuner: optimizes either the matrix instance, the thread count or both for the rsb_spmm operation.
The tuner works by evaluating different instances and working threads variants. The instance leading to faster operation time will be retained and given back to the user in *mtxOpp. If nrhs==1 and order==RSB_FLAG_WANT_COLUMN_MAJOR_ORDER, unitary stride vectors are assumed. In case of error, the original input matrix shall be unaffected. It is possible to specify the leading dimensions of Bp,Cp implicitly, with ldB=0 and ldC=0: in this case, their values will be computed internally and if Bp!=NULL,Cp!=NULL, they will be assumed of being sufficiently sized. Values of nrhs<1 will be treated as 1. Bp, Cp can be NULL: temporary vectors will be allocated, used, and deallocated within the tuner. If mtxOpp=NULL and *tnp!=NULL the best thread count will be probed for the matrix given in mtxAp. Please note that if threads-only tuning is requested and matrix has too few leaves (see RSB_MIF_LEAVES_COUNT__TO__RSB_BLK_INDEX_T), tuning will not work. If mtxAp==NULL, then the *mtxOpp instance will be used; however in this case, if a better instance is found, the original will be destroyed as with rsb_mtx_free(). The case mtxAp!=NULL&&*mtxOpp!=NULL is illegal and will cause error code RSB_ERR_BADARGS to be returned.
- Parameters
-
mtxOpp Optimal matrix structure pointer will be assigned to *mtxOpp(it may occur that *mtxOpp==mtxAp on output). IfmtxOppisNULLthen no data structure optimization will be attempted; rather, only optimal threads search will occur (tnpmust be notNULLthen).sfp Achieved speedup factor will be written to *sfp(unlesssfp==NULL).tnp If tnp==NULLon input, the current thread count will be utilized. Otherwise, if*tnp>0, then *tnp will be used as first suggestion in optimal thread count searching. Iftnp!=NULL,on output*tnpwill be set to contain the optimal number of threads. Then, the user is expected to set this number of threads using e.g.:RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_SET(RSB_IO_WANT_EXECUTING_THREADS,tnp,errval). Please note that this will affect the whole library operation, not only this matrix.maxr Optimizer rounds max count. If <1, will be treated as 1; if 0 will be decided automatically. Max is RSB_CONST_MAX_TUNING_ROUNDS.maxt Maximum time (in seconds) per optimization round (does not take in account conversion time). If maxt<0.0is provided,-ceil(maxt) will be interpreted as number of iterations to check for each operation time sample. Ifmaxt==0.0is provided, a default choice will be made instead.transA Transposition parameter for  (see matrix_transposition_flags_section).
(see matrix_transposition_flags_section). alphap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value (of the same type as matrix).mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. nrhs The number of right hand side vectors (cannot be <1).order A flag among RSB_FLAG_WANT_COLUMN_MAJOR_ORDER and RSB_FLAG_WANT_ROW_MAJOR_ORDER. For contiguous vector arrays, you probably want RSB_FLAG_WANT_COLUMN_MAJOR_ORDER. Bp The input vector array. If NULL, a temporary, internally allocated copy will be used.ldB Leading dimension of Bparray.betap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value.Cp The output vector array. If NULL, a temporary, internally allocated copy will be used.ldC Leading dimension of Cparray.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
Examples:
- Warning
- This function is still experimental. In case of error, although the matrix shall be unaffected, the library status may be affected (e.g.: execution thread count, default matrix subdivision).
- Todo:
- Autotuning functionality is still object of much research. Need support for lightweight, threads-only optimization.

| 
|
- See also
- rsb_spmv, rsb_spmm, rsb_spata, rsb_tune_spmm
◆ rsb_tune_spsm()
| rsb_err_t rsb_tune_spsm | ( | struct rsb_mtx_t ** | mtxOpp, |
| rsb_real_t * | sfp, | ||
| rsb_int_t * | tnp, | ||
| rsb_int_t | maxr, | ||
| rsb_time_t | maxt, | ||
| rsb_trans_t | transA, | ||
| const void * | alphap, | ||
| const struct rsb_mtx_t * | mtxAp, | ||
| rsb_coo_idx_t | nrhs, | ||
| rsb_flags_t | order, | ||
| const void * | Bp, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | ldB, | ||
| const void * | betap, | ||
| void * | Cp, | ||
| rsb_nnz_idx_t | ldC | ||
| ) |
An auto-tuner: optimizes either the matrix instance, the thread count or both for the rsb_spsm operation.
The tuner works by evaluating different instances and working threads variants. The instance leading to faster operation time will be retained and given back to the user in *mtxOpp. If nrhs==1 and order==RSB_FLAG_WANT_COLUMN_MAJOR_ORDER, unitary stride vectors are assumed. In case of error, the original input matrix shall be unaffected. It is possible to specify the leading dimensions of Bp,Cp implicitly, with ldB=0 and ldC=0: in this case, their values will be computed internally and if Bp!=NULL,Cp!=NULL, they will be assumed of being sufficiently sized. Values of nrhs<1 will be treated as 1. Bp, Cp can be NULL: temporary vectors will be allocated, used, and deallocated within the tuner. If mtxOpp=NULL and *tnp!=NULL the best thread count will be probed for the matrix given in mtxAp. Please note that if threads-only tuning is requested and matrix has too few leaves (see RSB_MIF_LEAVES_COUNT__TO__RSB_BLK_INDEX_T), tuning will not work. If mtxAp==NULL, then the *mtxOpp instance will be used; however in this case, if a better instance is found, the original will be destroyed as with rsb_mtx_free(). The case mtxAp!=NULL&&*mtxOpp!=NULL is illegal and will cause error code RSB_ERR_BADARGS to be returned.
- Parameters
-
mtxOpp Optimal matrix structure pointer will be assigned to *mtxOpp(it may occur that *mtxOpp==mtxAp on output). IfmtxOppisNULLthen no data structure optimization will be attempted; rather, only optimal threads search will occur (tnpmust be notNULLthen).sfp Achieved speedup factor will be written to *sfp(unlesssfp==NULL).tnp If tnp==NULLon input, the current thread count will be utilized. Otherwise, if*tnp>0, then *tnp will be used as first suggestion in optimal thread count searching. Iftnp!=NULL,on output*tnpwill be set to contain the optimal number of threads. Then, the user is expected to set this number of threads using e.g.:RSB_REINIT_SINGLE_VALUE_SET(RSB_IO_WANT_EXECUTING_THREADS,tnp,errval). Please note that this will affect the whole library operation, not only this matrix.maxr Optimizer rounds max count. If <1, will be treated as 1; if 0 will be decided automatically. Max is RSB_CONST_MAX_TUNING_ROUNDS.maxt Maximum time (in seconds) per optimization round (does not take in account conversion time). If maxt<0.0is provided,-ceil(maxt) will be interpreted as number of iterations to check for each operation time sample. Ifmaxt==0.0is provided, a default choice will be made instead.transA Transposition parameter for  (see matrix_transposition_flags_section).
(see matrix_transposition_flags_section). alphap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value (of the same type as matrix).mtxAp Valid rsb_mtx_tpointer to matrix representation.
representation. nrhs The number of right hand side vectors (cannot be <1).order A flag among RSB_FLAG_WANT_COLUMN_MAJOR_ORDER and RSB_FLAG_WANT_ROW_MAJOR_ORDER. For contiguous vector arrays, you probably want RSB_FLAG_WANT_COLUMN_MAJOR_ORDER. Bp The input vector array. If NULL, a temporary, internally allocated copy will be used.ldB Leading dimension of Bparray.betap Optional pointer (if NULL, will default to 1) to a numerical value.Cp The output vector array. If NULL, a temporary, internally allocated copy will be used.ldC Leading dimension of Cparray.
- Returns
- RSB_ERR_NO_ERROR on correct operation, an error code otherwise. You can use rsb_strerror_r() or rsb_perror() to get more information about the error.
If –enable-zero-division-checks-on-solve was specified at configure time, attempts to solve a triangular matrix with zeroes on a diagonal will fail.
- Warning
- This function is still experimental. In case of error, although the matrix shall be unaffected, the library status may be affected (e.g.: execution thread count, default matrix subdivision).
- Todo:
- Autotuning functionality is still object of much research. Need support for lightweight, threads-only optimization.

| 
|
- See also
- rsb_spsm, rsb_spsv, rsb_tune_spsm
- rsb_tune_spmm
 1.8.13
1.8.13